Snell's Law
Reflection behaves according to Snell's law which states:
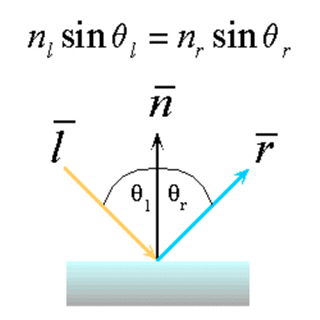
- The incoming ray, the surface normal, and the reflected ray
all lie in a common plane.
- The angle that the reflected ray forms with the surface normal
is determined by the angle that the incoming ray forms with the
surface normal, and the relative speeds of light of the mediums
in which the incident and reflected rays propogate according to
the following expression.
(Note: nl and nr are the indices of refraction)
Reflection is a very special case of Snell's Law where the incident
light's medium and the reflected rays medium is the same. Thus we can
simplify the expression to:
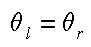
|