Reinforcement Learning for Mapping Instructions to Actions
S.R.K. Branavan, Harr Chen, Luke Zettlemoyer, Regina Barzilay
 Paper
Paper
 Slides
Slides
 Paper
Paper
 Slides
Slides
During the reinforcement learning process, the learner maps each instruction document to a candidate sequence of actions, executes them in the target environment (in this case the Windows 2000 user interface), and learns from how well these candidate actions work. For this process to work, the learner needs to be able to control the Windows 2000 operating system in two ways:
| 1. | Reset the Windows 2000 OS to some specified initial state | |
| 2. | Execute selected action sequences in the Windows 2000 user interface, and observe the resulting changes. |
The first requirement is met by running the Windows 2000 operating system on a virtual machine. In our experiments, VMware Workstation (http://www.vmware.com) was used as the virtualization software - but this was simply due to familiarity, and any alternatives should be equally good for this purpose. The initial state to which the OS needs to be reset was saved as a virtual machine snapshot. Then the command line interface of VMware was used to programmatically reset the virtual machine to this snapshot when necessary. The reinforcement learner gets access to the VMware command line through the VM snapshot reset process.
The requirement of being able to observe the current state of the Windows 2000 user interface, and to execute selected user interface actions was achieved through the operating system instrumentation agent. This program when run in the target Windows 2000 OS, connects to the reinforcement learner through a TCP/IP socket connection, and commnicates with it using a simple human readable protocol. Through this agent, the learner is able to retrieve the current set of user interface objects along with their attributes, and also execute user interface commands on these objects.
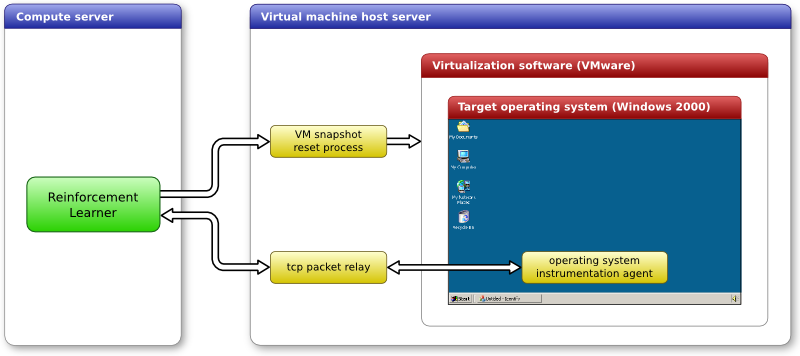
|
Figure 1. This diagram shows the complete framework used in the Windows 2000 experiments.
| 1. | Reinforcement Learner
[  code ]
[ code ]
[  configuration ] configuration ]
| ||||
|
Command line : python run.py learner.cfg This is the reinforcement learner source code for the Windows 2000 application. | |||||
| 2. | VM snapshot reset process
[  code ] code ] | ||||
|
Command line : python vm_snapshot_reset_process.py 5002 This program allows the reinforcement learner to reset the Windows 2000 setup to
an initial state through the command line interface of VMware. This code will
need to be re-written if different virtualization software is used. If VMware is
used, the following line in the code will need to be modified to point to the
vmx file of your virtual machine: The number specified on the command line (5002) is the TCP/IP port on which the learner will attempt to connect to this process. This value needs to correspond to the port specified in the learner configuration file. The default value is 5002. | |||||
| 3. | TCP packet relay
[  code ] code ] | ||||
|
Command line : python tcp_packet_relay.py 5000 This program is a simple TCP/IP packet relay. It allows the reinforcement learner to connect to the os instrumentation agent while insulating it from the effects of the virtual machine being reset. The number specified on the command line (5000) is the TCP/IP port on which the learner will attempt to connect to this process. This value needs to correspond to the port specified in the learner configuration file. The default value is 5000. | |||||
| 4. |
| ||||
|
This program is run by double-clicking on interact.exe from the Windows file explorer. This program when run in Windows 2000 allows the reinforcement learner to observe and interact with the user interface of the operating system, and of the applications running in it. Currently it is only able to observe and interact with user interface objects that are part of the standard Windows 2000 UI library. Interaction with other UI objects was not attempted due both to lack of documentation, and to the peculiarities of their APIs. |
| 1. | The current version of the operating system instrumentation agent is only able to observe and interact with user interface objects that are part of the standard Windows 2000 UI library. Interaction with other UI objects was not attempted due both to lack of documentation, and to the peculiarities of their APIs. |
| 2. | Windows 2000 was selected as the target operating system both for ease of instrumentation, and availability of help documents. |
| 3. | During a normal learning run, the Windows 2000 virtual machine will be reset multiple times. At every reset, the TCP/IP connection from the operating system instrumentation agent to the reinforcement learner will be interrupted. The tcp packet relay process is used to insulate the learner from this repeated socket disconnection/reconnection. |
| 4. | In our experiments, simply for the sake of convenience and flexibility, the learner and the virtual machine were run on different compute hardware. This is the setup shown in Figure 1. However, both processes can be run on a single compute server if hardware resources are sufficient. |
| 5. | For the sake of performance, no anti-virus or firewall was installed on the Windows 2000 setup. To keep the operating system safe from attack, the virtual machine was setup to disallow network connectivity to the external world. Network connections from Windows 2000 were only allowed to the server on which the virtual machine was running (i.e. "local network only"). |
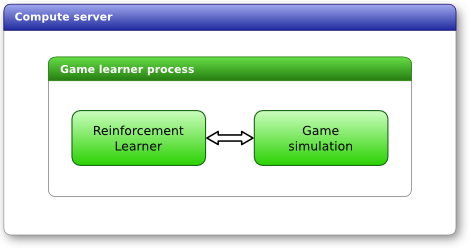
|
Figure 2. This diagram shows the complete framework used in the puzzle game experiments.
| 1. | Game learner
[  complete archive ] complete archive ]
|
|
Command line : ./run.sh This is a comlete archive for the puzzle game application containing source, data, and configuration. |
The source code for this work can be downloaded from the links below.
| Reinforcement Learner |
[  code ]
[ code ]
[  configuration ] configuration ]
| |
| VM snapshot reset process |
[  code ] code ] | |
| TCP packet relay |
[  code ] code ] | |
| Operating system instrumentation agent |
[  code ]
[ code ]
[  compiled binary ]
[ compiled binary ]
[  runnable bundle (including dlls) ] runnable bundle (including dlls) ]
| |
[  configuration ] configuration ]
|
The Windows instumentation framework requires Visual C++ to compilation. It was developed and tested using Visual C++ (version), but does not use any version specific functionality. Therefore it should operate correctly if compiled using any recent version of VC++. The code uses the MFC library, but can be modified to be not dependent on them if necessary.
| Game learner process |
[  code ]
[ code ]
[  configuration ] configuration ]
|
Note that this is only the source code for the learner in the puzzle game domain. A complete runnable archive of code, data and configurations is listed under "Puzzle game experimental framework" above.
The datasets used in this work are available in text format from the link below:
[ Microsoft Help & Support Windows 2000 dataset ] source: support.microsoft.comThe gold standard annotations for the windows dataset are available from the links below:
[ Annotations for Microsoft Help & Support Windows 2000 dataset ]The gold standard annotations for the puzzle dataset are available from the links below:
[ Annotations for puzzle dataset ]