 |
|
|
|
|
Vision-Aided
Acoustic Processing
This
project integrates microphone arrays and cameras for
use in perceptive environments. The ceiling-mounted
microphone array uses slight differences in audio
signals at different microphones to amplify sounds
coming from selected locations in the room. The array
allows for multiple audio sources to be separated
and allows users to interface speech recognition systems
without the user of a close-talking microphone. More...
|
 |
|
Photograph
of environment with microphones and camera locations
highlighted.
|
|
|
|
Person
Tracking with Stereo Range Sensors
Three
camera modules, each consisting of stereo camera and a computer,
are situated in the room. The cameras are arranged to view
the entire room and continually estimate 3D-point clouds
of the objects in the room. Foreground points are passed
to an integration module which clusters the points into
blobs that represent people. From these blobs, features
such as person location and posture are extracted. More...
|
 |
|
View from
one of the camera modules. It consists of an intensity,
disparity, foreground, and ground plane images .
|
|
|
Communication
Via Eye Blinks
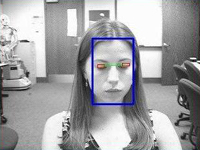
A
real-time vision system that is intended to provide an alternate
input modality to allow people with severe disabilities
to access a computer. The system automatically detects a
user's blinks and accurately measures their duration. Voluntary
long blinks trigger mouse clicks while involuntary short
blinks are ignored. The system enables communication using
blink patterns: sequences of long and short blinks which
are interpreted as semiotic messages. (Collaborative project)
More...
|
 |
|
Detecting
eye blinks and automatically distinguishing between involuntary
blinks and voluntary periods of closure enables users to
communicate without the keyboard and mouse.
|
|
|
Interactive
Wall
This
project examines the interaction between physical and perceptual
interfaces in games and virtual environments. Estimates
of body position and pose are the raw measurements of this
perceptual interface but must be transformed into abstractions
of gesture, motion, and action and mapped to application
controls to be responsive as an input mechanism. The mapping
of recognized tokens to controls depends on both the application
and the structure of the physical space. More...
|
 |
|
Detection
of body position and arm pose using stereo segmentation
techniques.
|
|
|
View-Independent
HID
In
a constraint-free environment, where users move freely,
identification must be made view-independent so that no
particular pose of the user be required. It is a difficult
task for a system consisting of a small number of cameras
mounted in fixed locations since most of the recognition
schemes to date are not robust to significant pose invariance.
Our approach to this problem is based on the efficient algorithms
for constructing Image-Based Visual Hull, which allow rendering
a synthetic textured view of an object from arbitrary viewpoints.
We apply this methodology for gait and face recognition.
More...
|
  |
|
Synthetic
profile generated that can be used for gait recognition.
|
|
|
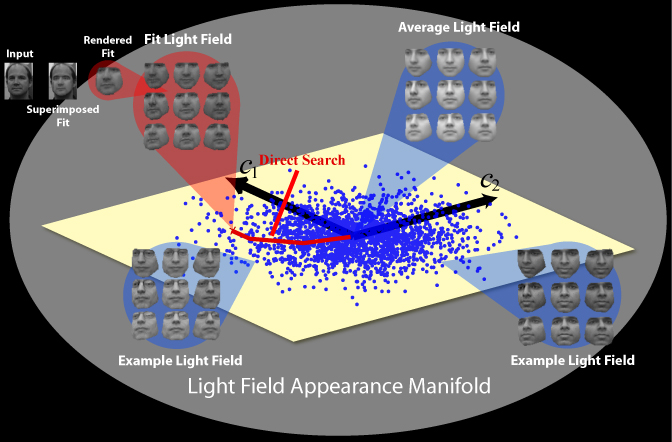
Light-Field Appearance Manifolds
We present a statistical, multi-view appearance model
using light-fields, a real-time image-based rendering
technique that can easily represent objects with non-Lambertian
surface reflectance and complex geometry. Our model is
able to rebuild an entire light-field representation of
an object from a single 2D image of an object imaged under
unknown pose. In turn, the object can be rendered under
previously unseen views. We demonstrate our method using
a head light-field data set and provide a comparison with
state-of-the-art techniques. More...
|
 |
|
Light-field
appearance manifold of the human head. (See project web-page
for full-size image)
|
|
|
 |