Global Illumination
Early on, in the development of computer graphics, ray-casting was recognized as
viable approach to 3-D rendering. However, it was generally dismissed because:
- Takes no advantage of screen space coherence
- Requires costly visibility computation
- Only works for solids
- Forces per pixel illumination evaluations
- Not suited for immediate mode rendering
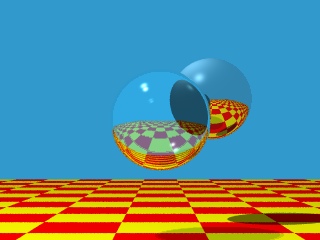
It was not until Turner Whitted (1980) recognized that recursive ray casting,
which has come to be called ray tracing, could be used to address
global illumination that interest in ray tracing became widespread.
|