Tricks Explained
In this method we did two critical things. We orient the edge equations, and we compute the bounding box.
From analytic geometry we know that the area of a triangle
{(x1,y1), (x2,y2), (x3,y3)} is:
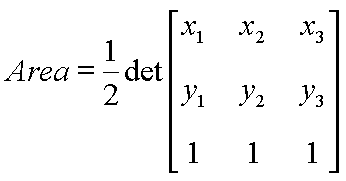
The area is positive if the vertices are counterclockwise and negative if clockwise
An aside:
In terms of our discriminator, what does a positive C imply?
|